Implantable Sensor to measure liquor pressure of a ventricular drainage system
- Increase of the intracranial pressure (ICP) in the skull may cause progressive enlargement of the head, convulsion, tunnel vision and mental disability due to shortage of oxygen and nutrients
- To reduce the intracranial pressure, the implantation of a drainage system (shunt) which removes excessive CSF, e.g. into the abdominal cavity, is necessary
- Wireless measurements of the cerebrospinal fluid pressure in the shunt
- Approved for use as a long-term implant in humans
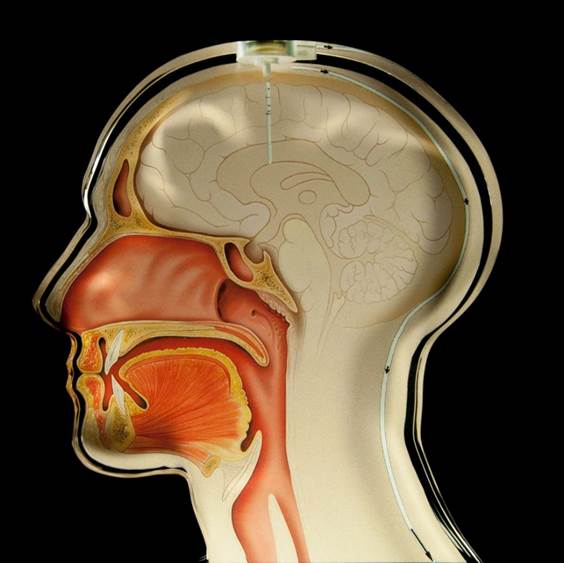
The human brain is filled with cerebrospinal fluid (CSF), which is produced in the entricles. Patients suffering from normal pressure hydrocephalus (NPH) produce more CSF than they resorb. This leads to an increase of the intracranial pressure (ICP) in the skull, what may cause progressive enlargement of the head, convulsion, tunnel vision and mental disability due to shortage of oxygen and nutrients. To reduce the intracranial pressure, the implantation of a drainage system (shunt) which removes excessive CSF, e.g. into the abdominal cavity, is necessary.
In corporation with two companies a system was developed for wireless measurements of the cerebrospinal fluid pressure in the shunt. The system is approved for use as a long-term implant in humans.
 Fraunhofer Group for Microelectronics in cooperation with the Leibniz institutes IHP and FBH
Fraunhofer Group for Microelectronics in cooperation with the Leibniz institutes IHP and FBH