Sustainable information and communication technology
It stands to reason that the highly dynamic international ICT market, increasing in the wake of digitization, must make its own significant and measurable contribution to achieving climate protection targets. However, this can only be achieved if overall systems and their networking over the entire lifecycle are included in the consideration in addition to individual components. The "Green ICT @ FMD" competence center, which was launched in August 2022, is working intensively on the following key areas:
- Resource-efficiency in sensor edge cloud systems
- Energy-saving communication infrastructures
- Resource-optimized electronics production
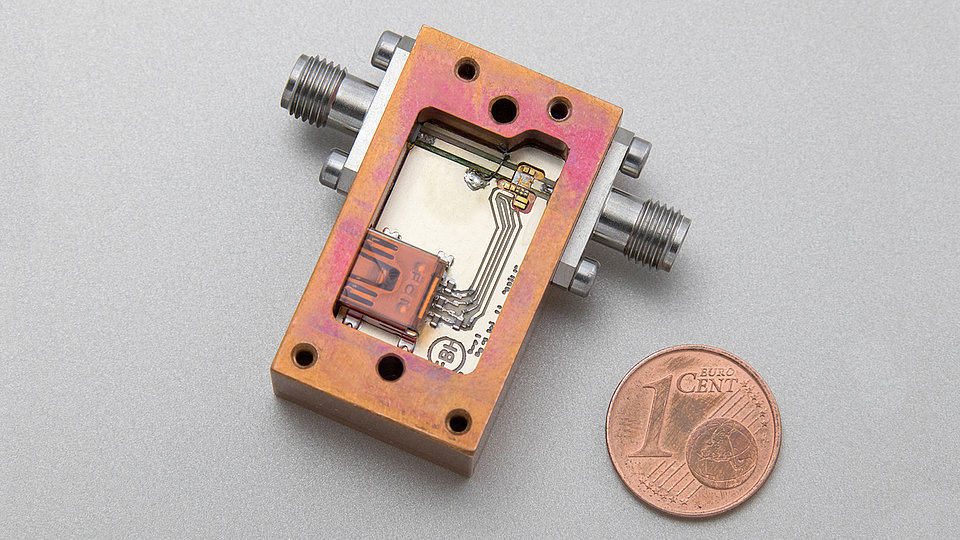
 Fraunhofer Group for Microelectronics in cooperation with the Leibniz institutes IHP and FBH
Fraunhofer Group for Microelectronics in cooperation with the Leibniz institutes IHP and FBH